Tribune Group GmbH Inc.
Tribune Group GmbH Inc.
Nationally Approved PACE Program
Provider for FAGD/MAGD credit.
Approval does not imply acceptance by
any regulatory authority or AGD endorsement.
7/1/2024 - 6/30/2028.
Provider ID# 355051
The use of MTA-based endodontic cements in root perforation treatment
Sponsor: Angelus
Author: Nayara Rodrigues Nascimento Oliveira Tavares
Co-author: Jéssica Monteiro Mendes, Alexia da Mata Galvão, Maria Antonieta Veloso Carvalho de Oliveira.
RESUME
Patient, 28 years, male, attended to the dental clinic for making a full crown on element 46. Through radiographic examinations, it was possible to verify the presence of extensive lesion in the furcal region (Figure 1A). In the first session, resin reconstruction was performed to facilitate insulation, perforation location (Figure 1B) and placement of intracanal dressing based on calcium hydroxide.
After 15 days, the endodontic retreatment was started. With canals already prepared (Figure 2), new dressing was placed in the canals and perforation, followed by temporary restoration.
After 30 days, the intracanal dressing was removed and the perforation was sealed with MTA-based reparative cement (MTA Repair HP, Angelus) (Figure 3). The insertion was done with a small MTA Applicator and adapted with a condenser (Figure 4). After checking the adaptation of reparative cement, the canals were sealed with MTA-based endodontic sealer (MTA-Fillapex) and gutta-percha cones using the lateral condensation technique (Figure 5).
Radiographically, it was observed satisfactory sealing and extravasation of the MTA-based reparative cement (Figure 6). The tooth was provisionally restored and sent to rehabilitation with full crown.
IMAGES
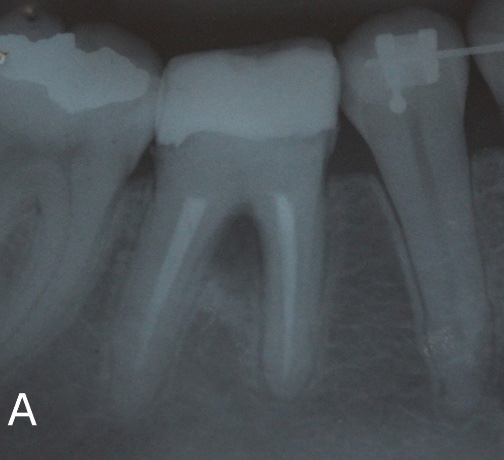
Figure 1: Initial clinical and radiographic aspects.
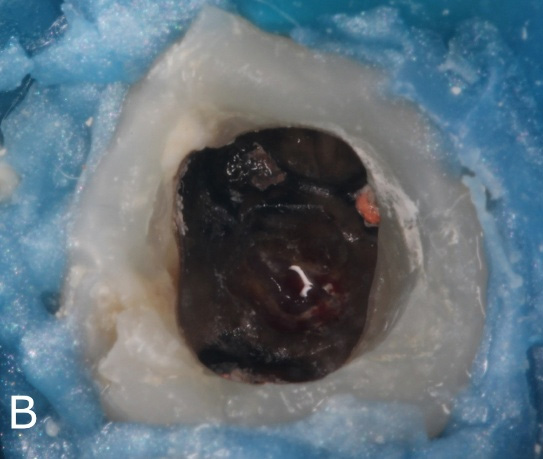
Figure 1: Initial clinical and radiographic aspects.
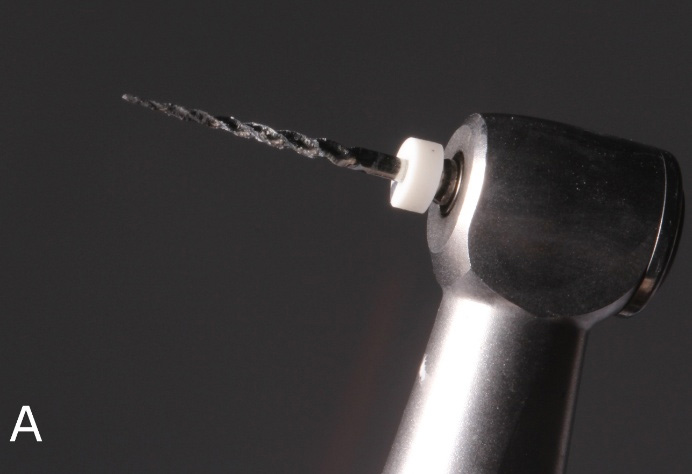

Figure 2: Removal of the sealing material for retreatment.
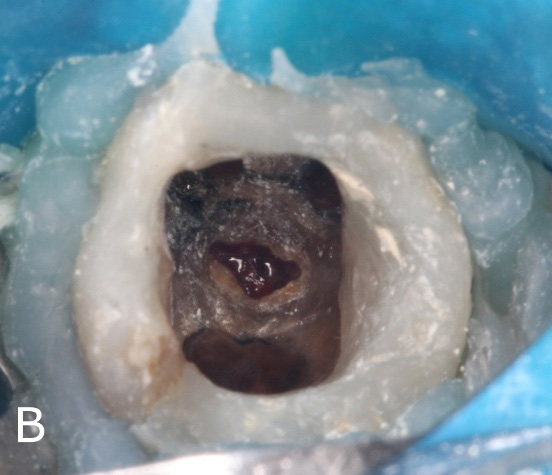
Figure 2: Removal of the sealing material for retreatment.
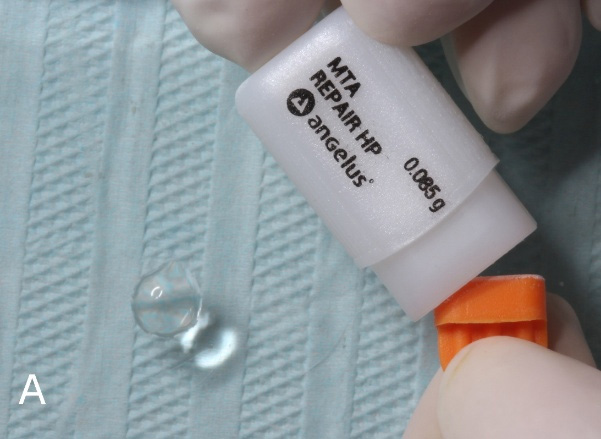
Figure 3: Manipulation of the reparative cement MTA REPAIR HP and manipulated cement.
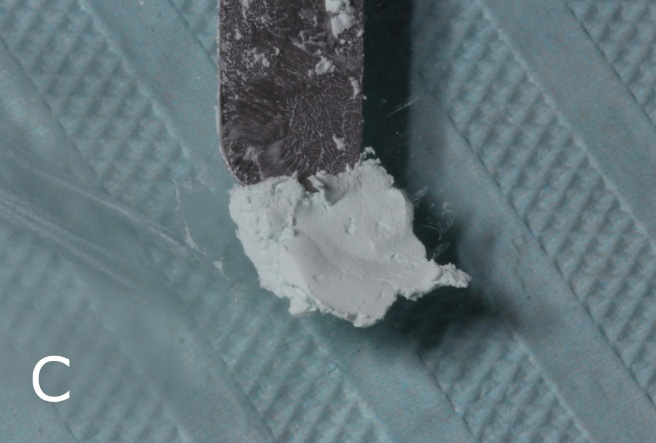

Figure 3: Manipulation of the reparative cement MTA REPAIR HP and manipulated cement.
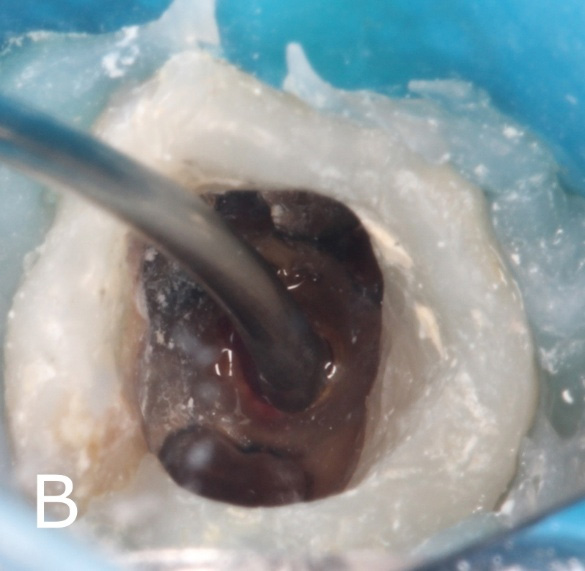
Figure 4: Insertion in the perforation with MTA Applicator and perforation filled by the cement.
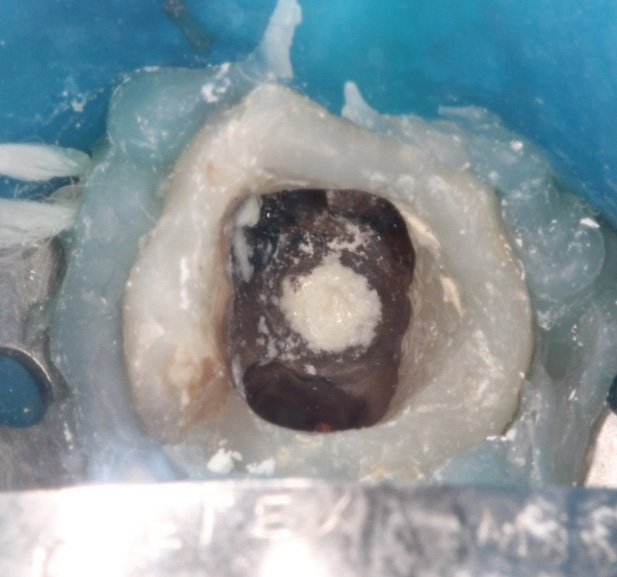
Figure 4: Insertion in the perforation with MTA Applicator and perforation filled by the cement.

Figure 5: Seal with MTA-based cement.
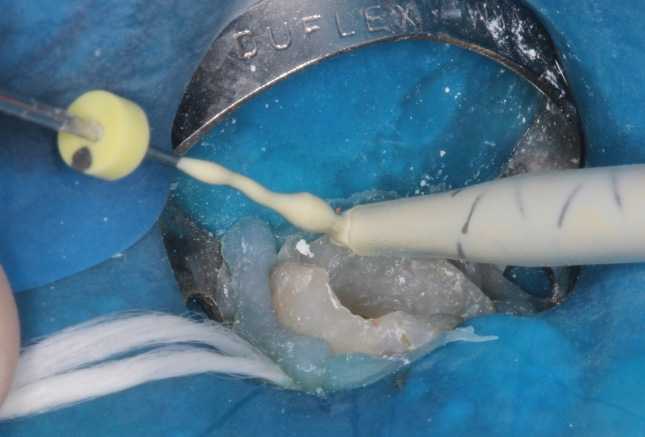

Figure 5: Seal with MTA-based cement.
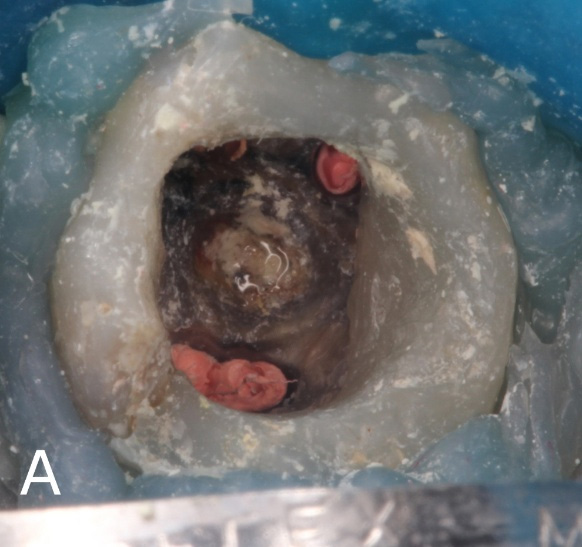
Figure 6: Final clinical and radiographic aspects.
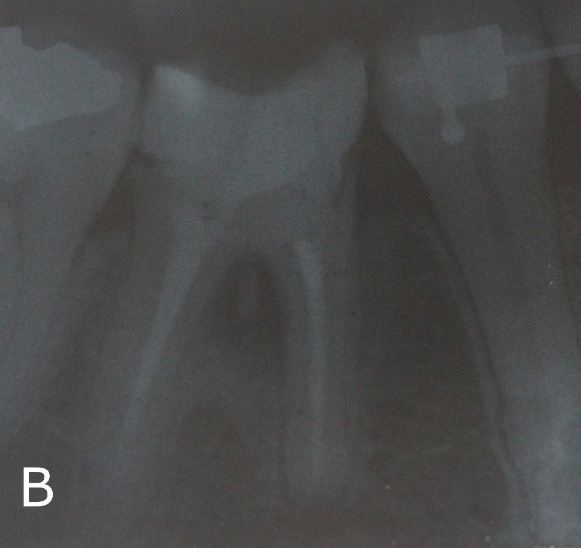
Figure 6: Final clinical and radiographic aspects.